Twitter is one of the most popular social networking services used by most prominent people of world. Tweets can be used to perform sentimental analysis.
In this article we will see how to scrape tweets using BeautifulSoup. We are not using Twitter API as most of the APIs have rate limits.
You can download all the pictures of any Instagram user in just few lines of codes. We converted the script into reusable python package to make things easy.
Setup:
Create a virtual environment. If you are not in the habit of working with virtual environments, please stop immediately and read this article on virtual environments first.
Once virtual environment is created and activated, install the dependencies in it.
pip install beautifulsoup4==4.6.0 bs4==0.0.1 requests==2.18.4
Analysing Twitter Web Requests:
Lets say we want to scrape all the tweets made by Honourable Prime Minister of India, Shri Narendra Modi.Go to the browser, I am using Chrome, press F12 to open the debugging tool.
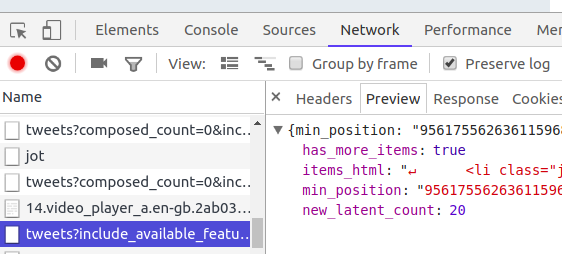
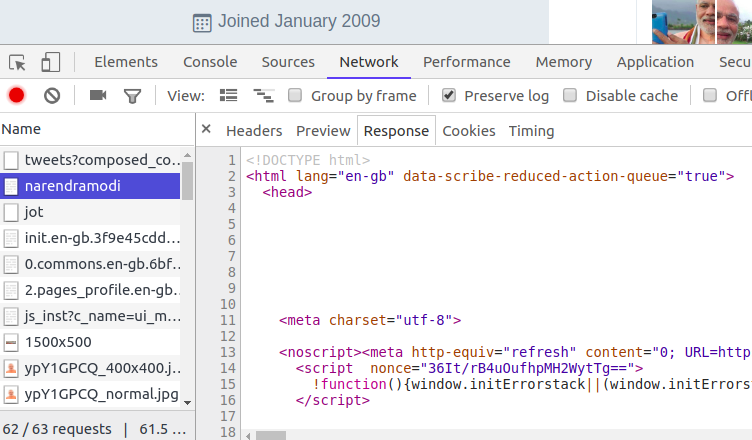
Now go the the URL https://twitter.com/narendramodi. In the network tab of debugging tool, you will see the response of request made to URL /narendramodi.
Response is an HTML page. We will convert this HTML response into a BeautifulSoup object and will extract the tweets.
If you scroll down the page to load more tweets, you will see more requests being sent where response is not simple HTML but is in JSON format.
Extracting tweets from HTML content:
First inspect the tweet element on web page. You will see that all the tweets are enclosed inli HTML tag. Actual tweet text is inside a p tag which is the descendent of li tag.
We will first get all the li tags and then p tags from each li tag. Text contained in the p tag is what we need.
Code to start with:
# script to scrape tweets by a twitter user.
# Author - ThePythonDjango.Com
# dependencies - BeautifulSoup, requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import sys
import json
def usage():
msg = """
Please use the below command to use the script.
python script_name.py twitter_username
"""
print(msg)
sys.exit(1)
def get_username():
# if username is not passed
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
usage()
username = sys.argv[1].strip().lower()
if not username:
usage()
return username
def start(username = None):
username = get_username()
url = "http://www.twitter.com/" + username
print("\n\nDownloading tweets for " + username)
response = None
try:
response = requests.get(url)
except Exception as e:
print(repr(e))
sys.exit(1)
if response.status_code != 200:
print("Non success status code returned "+str(response.status_code))
sys.exit(1)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'lxml')
if soup.find("div", {"class": "errorpage-topbar"}):
print("\n\n Error: Invalid username.")
sys.exit(1)
tweets = get_tweets_data(username, soup)
We will start with start function. First collect the username from command line and then send the request to twitter page.
If there is no exception and status code returned in response is 200 i.e. success, proceed otherwise exit.
Convert the response text into BeautifulSoup object and see if there is any div tag in the HTML with class errorpage-topbar. If yes that means the username is invalid. Although this check is not required because in case of invalid username, 404 status is returned which will be checked in status_code check condition.
Extract tweet text:
def get_this_page_tweets(soup):
tweets_list = list()
tweets = soup.find_all("li", {"data-item-type": "tweet"})
for tweet in tweets:
tweet_data = None
try:
tweet_data = get_tweet_text(tweet)
except Exception as e:
continue
#ignore if there is any loading or tweet error
if tweet_data:
tweets_list.append(tweet_data)
print(".", end="")
sys.stdout.flush()
return tweets_list
def get_tweets_data(username, soup):
tweets_list = list()
tweets_list.extend(get_this_page_tweets(soup))
As discussed, we first find out all li tags and then for each element we try to get tweet text out of that li tag.
We keep printing a dot on screen every time a tweet is scrapped successfully to show the progress otherwise user may think that script is doing nothing or is hanged.
def get_tweet_text(tweet):
tweet_text_box = tweet.find("p", {"class": "TweetTextSize TweetTextSize--normal js-tweet-text tweet-text"})
images_in_tweet_tag = tweet_text_box.find_all("a", {"class": "twitter-timeline-link u-hidden"})
tweet_text = tweet_text_box.text
for image_in_tweet_tag in images_in_tweet_tag:
tweet_text = tweet_text.replace(image_in_tweet_tag.text, '')
return tweet_text
We sometimes have images inside tweets, we will discard those images as of now. We do this by getting image tags inside tweets and replacing image text by empty string.
Scrapping more tweets:
So far we were able to get tweets from first page. As we load more pages, when scrolling down, we get JSON response. We need to parse JSON response, which is slightly different.
def get_tweets_data(username, soup):
tweets_list = list()
tweets_list.extend(get_this_page_tweets(soup))
next_pointer = soup.find("div", {"class": "stream-container"})["data-min-position"]
while True:
next_url = "https://twitter.com/i/profiles/show/" + username + \
"/timeline/tweets?include_available_features=1&" \
"include_entities=1&max_position=" + next_pointer + "&reset_error_state=false"
next_response = None
try:
next_response = requests.get(next_url)
except Exception as e:
# in case there is some issue with request. None encountered so far.
print(e)
return tweets_list
tweets_data = next_response.text
tweets_obj = json.loads(tweets_data)
if not tweets_obj["has_more_items"] and not tweets_obj["min_position"]:
# using two checks here bcz in one case has_more_items was false but there were more items
print("\nNo more tweets returned")
break
next_pointer = tweets_obj["min_position"]
html = tweets_obj["items_html"]
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
tweets_list.extend(get_this_page_tweets(soup))
return tweets_list
First we check if there are more tweets. If yes then we find the next pointer and create the next URL. Once JSON is received, we take out the items_html part and repeat the process of creating soup and fetching tweets.
We keep doing this until there are no more tweets to scrap. We know this by looking at the variable has_more_items and min_position in JSON response.
Complete script:
Now all the functions are completed. Let put them together.Download the complete script from GitHub.
Running the script:
Assuming you have installed dependencies in virtual environment, lets run the script.(scrappingvenv) rana@Nitro:python_scripts$ python tweets_scrapper.py narendramodi Downloading tweets for narendramodi ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ No more tweets returned Dumping data in file narendramodi_twitter.json 844 tweets dumped. (scrappingvenv) rana@Nitro:python_scripts$
You might introduce some wait between requests if you get any rate limit errors.
Dumping data in file:
You might want to dump the data in text file. I prefer dumping data in JSON format.# dump final result in a json file
def dump_data(username, tweets):
filename = username+"_twitter.json"
print("\nDumping data in file " + filename)
data = dict()
data["tweets"] = tweets
with open(filename, 'w') as fh:
fh.write(json.dumps(data))
return filename
Let us know if you face any issues.